Operations
Clone
Cloning creates a local repository (on your computer) from a remote repository say on Gitlab or GitHub. You cannot contribute back to the source repository unless you are added as an collaborator or you own it. For this module, we will only clone a repository so we may have a local working copy. We will clone in the Pipeline section.
Fork
When you fork a repository, you make a copy of someone else’s cloud repository (i.e Gitlab) to your cloud repository. There will be a connection between the forked repository and yours so you may contribute back (merge requests). You may also pull updates from the source repository into your fork.
I have a public repository that you can Fork here
Origin and Upstream
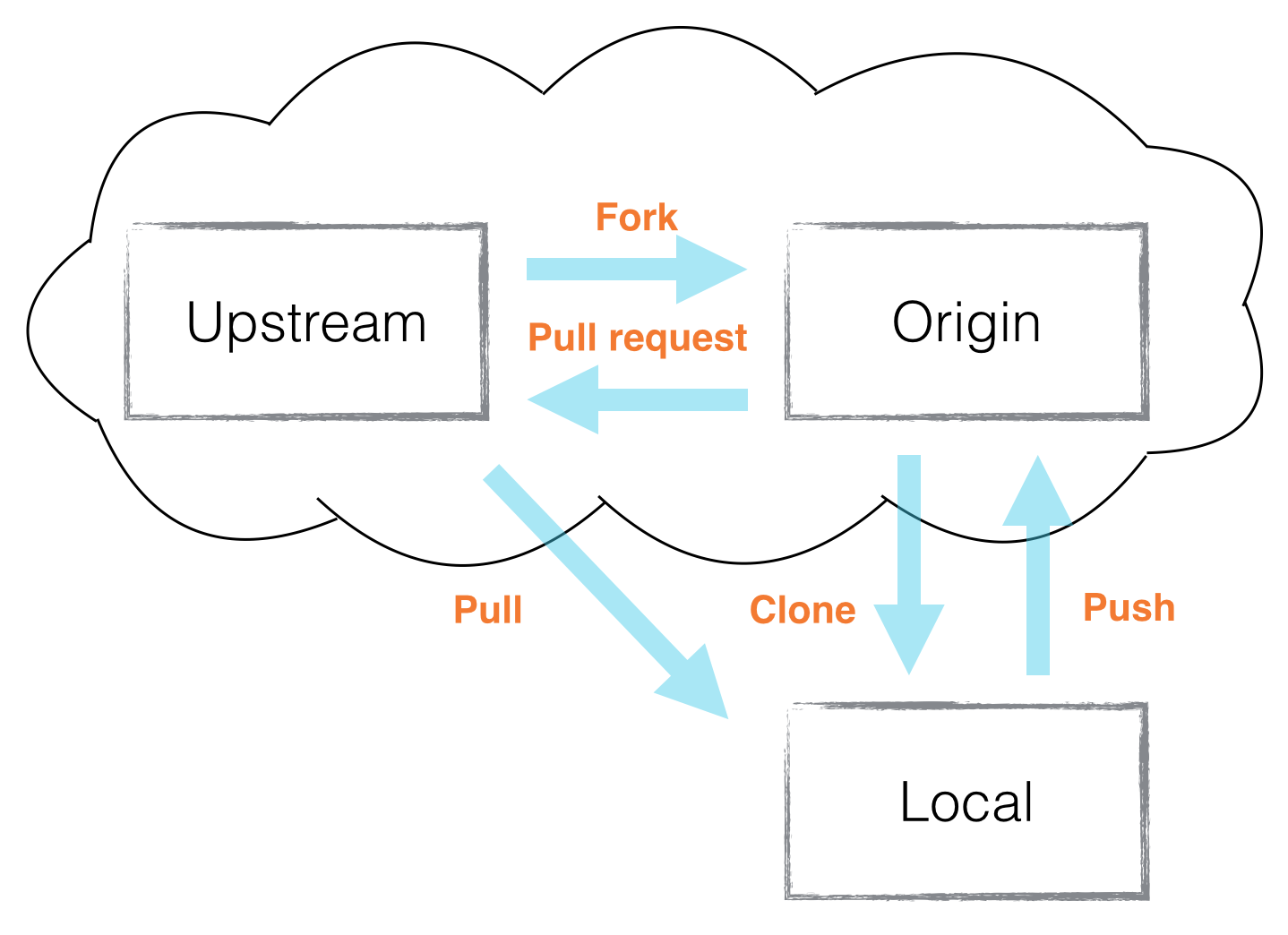
Fig 10
Let’s check what remotes (if any) you currently have in your local repository
Note
If you cloned a repository you will have your origin listed
git remote -v
Origin
Your own repository (i.e. git@gitlab.com:your_username/your_reposity.git )
To set an origin (and origin is just a name space, could easy be just your name)
git remote add origin git@gitlab.com:<username>/<repo>.git
Upstream
The source repository you’re forked from (i.e. git@gitlab.com:someonelse_username/their_reposity.git )
To set an upstream:
git remote add upstream https://gitlab.com/someonelse_username/their_reposity.git
Let’s view our remote’s now
git remote -v
origin git@gitlab.com:your_username/ansible_lab.git (fetch)
origin git@gitlab.com:your_username/ansible_lab.git (push)
upstream https://gitlab.com/cwise24/ansible_lab.git (fetch)
upstream https://gitlab.com/cwise24/ansible_lab.git (push)
In case you make a mistake adding an upstream or origin (destination)
git remote rm <destination>
Pull Request or Merge Request
Now comes time to merge your work back into the Upstream branch or to accept a merge request(Gitlab/BitBucket) or a Pull Request(GitHub) from a forked contributor
Create a Merge Request
To create a merge request, from your repository on left side click Merge Request

Fig 11
Then click New merge request

Fig 12
You must view the compare branches before you can submit

Fig 13
Click Submit Merge Request

Fig 14
Your submitted Merge Request

Fig 15
Accepting a Merge Request

Fig 16

Fig 17

Fig 18
Pull from Upstream
To keep your local (and origin) in sync with the upstream repository, you’ll want to do either a fetch or pull
git fetch upstream <branch>
git pull upstream <branch>
Cleaning Up
When you have to delete files from your project, it can cause some issues. And since git is making snapshots with every commit, you may find .bak files in your repository
git rm -r <directory>
git rm <file>
Now that the file is staged
git commit -m "rm <file>"
git push origin <branch>
Git Clean, this is useful to remove untracked files (be sure to see the IMPORTANT banner below)
git clean -x -n
git clean -x -f
Important
Read notes on git clean before use (docs-> git clean)